
Understanding the Increasing Relevance of Choice Models for Advancing
Transportation Modelling in Smart Cities
![]()
Course Overview
The recent technological advances in the fields of transportation (such as automated/electric cars), sensing (sensors for physical health, and air quality) and mobility (ridesharing applications) provide a unique opportunity to transform existing urban and non-urban regions into “Smart Cities”. According to the World Bank, about 34% of Indian population lives in urban regions. It is estimated that 50% of the population will live in urban regions by 2030. Given the projected growth of urbanization, the Smart City Initiative of developing 100 smart cities across the country is quite timely. A successful Smart City will enable future urban populations to optimally allocate limited resources while meeting sustainability, health and resilience goals. The current course proposal will focus on training the academic, public and private professionals in India on choice modelling approaches that can enhance the knowledgebase of transportation modelling efforts useful for informing Smart City infrastructure installation and data analytics for installed smart city infrastructure.
With these aforementioned objectives, the proposed course will broadly consist of three modules. The first module will discuss how survey design methods and choice modelling approaches can be employed to understand smart city infrastructure adoption decisions at the individual, household and system levels. The second module will illustrate how emerging econometric and statistical modelling approaches can serve analytics needs of the vast data compiled by smart city infrastructure. Finally, the third module of the course will focus on how existing regional transportation planning methods will need to be customized with the advent of Smart City infrastructure and data analytics.
The content in this program will include a background of traditional transportation data collection methods, approaches for eliciting stated preference survey data and using advanced modelling methods for analysing the survey data. The course modules will also cover state of the art approaches for these different types of variables. Further, the course module will provide the participants an illustration of the advanced econometric models developed for analysing such data with case studies on bicycle sharing systems, ride hailing data, traffic speed distribution on roadways and incident clearance time prediction. The course will provide specific examples such as using mobile phone based or Bluetooth based origin destination matrices for model calibration or validation. Further, case studies on how smart phone mobility applications can be developed for easier activity data collection by embedding location and travel mode recognition will be discussed. Recent research on approaches employing mobile apps for data collection and model implementation will also be presented. It is expected that participants will attain sufficient knowledge in this area after attending this program.
Course Objectives
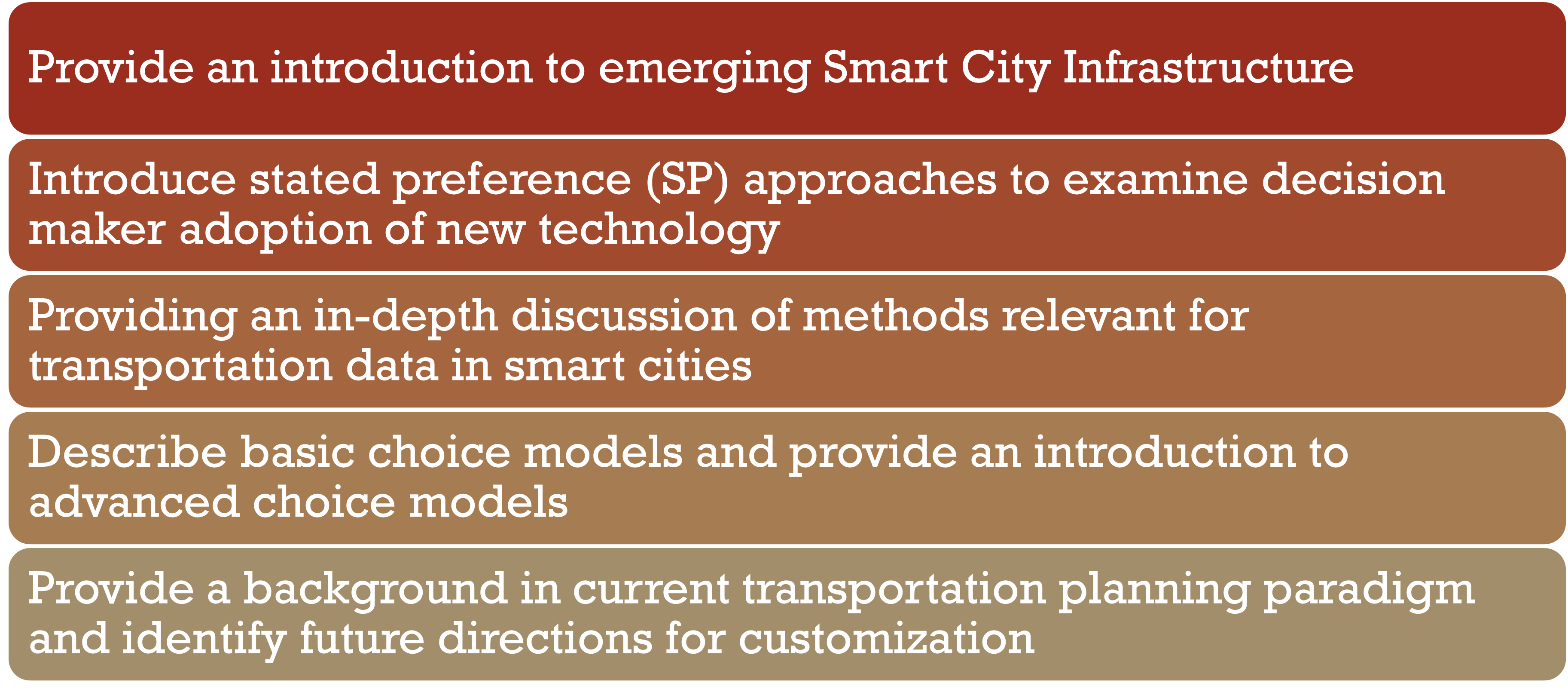
Course Modules
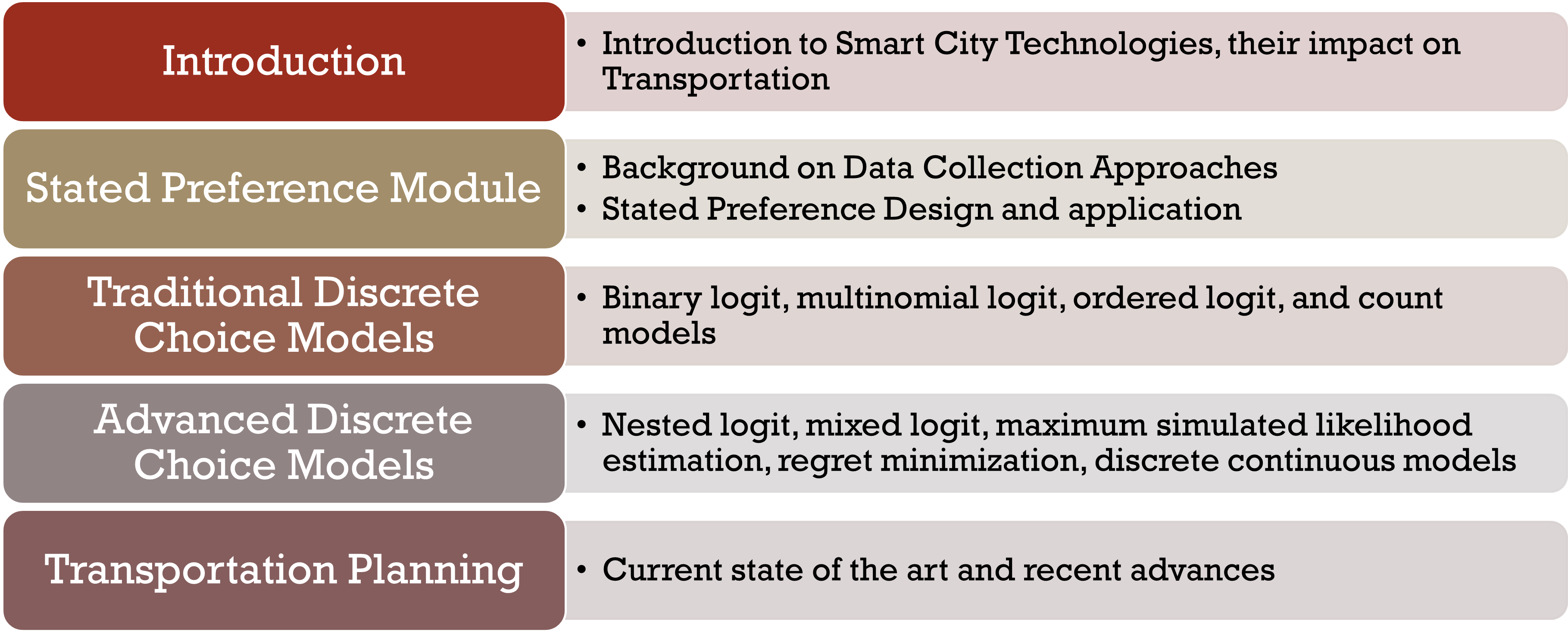
Course Material
The lecture notes, codes employed in the class and any other supplementary material is available here for download. The material is organized by module.
Module 1: Introduction
Module 2:Stated Preference Module
[Lecture Slide Deck]
[R Codes]
Module 3:Traditional Discrete Choice Models
[Lecture Slide Deck Part 1]
[Lecture Slide Deck Part 2]
[Binary Logit Apollo Codes]
[MNL Apollo Code]
[OL Apollo Codes]
[Tutorial Data] and [Data Description]
Module 4:Advanced Discrete Choice Models
[Lecture Slide Deck]
[Lecture Slide Deck Appendix 1: Copula Methods]
[Lecture Slide Deck Appendix 2: Fractional Split Models]
[Lecture Slide Deck Appendix 3: Grouped GOP Model]
[Nested Logit Apollo Codes]
[Mixed Logit Apollo Codes]
Module 5:Transportation Planning
[Lecture Slide Deck]
[Appendix 1]
[Appendix 2]
Please note that the codes are modified from Apollo Package in R for educational purposes. The user should carefully review the code and its results before using the files. We are not responsible for any errors. For more details refer to Hess, S. and Palma, D., 2019. Apollo: A flexible, powerful and customizable freeware package for choice model estimation and application. Journal of choice modelling, 32, p.100170